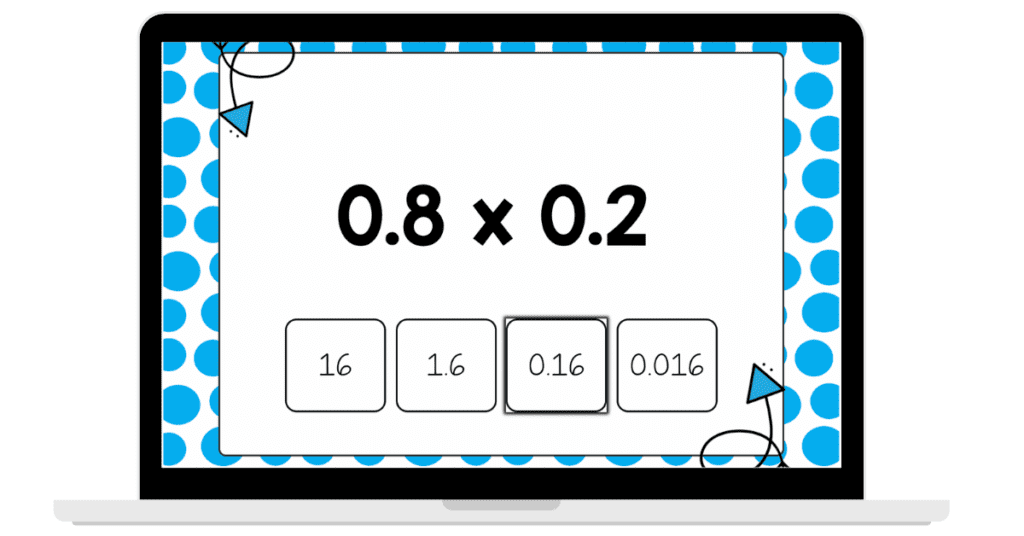
When I first had to teach multiplying using decimal models, I was overwhelmed. Growing up, I did math the “old way.” This modeling process stumped me. Now that I have taught students multiplying decimals using models, I completely understand the concept behind the modeling!
The fifth-grade common core math standard states that students should learn to multiplying decimals using concrete models or drawings. This standard expands upon decimal place value concepts taught previously. To learn more about teaching decimals, check out this post about modeling decimals. This other post about decimal misconceptions is also very helpful.
If you are looking for some easy-to-print decimal models you can use for multiplying decimals in your classroom, download our decimal models free pdf resource!
Breaking Down the Standard
Let’s unpack this standard. This particular standard is full of a ton of information and every operation, all including decimals. For the sake of this post, we will focus on the multiplication operation.
In this case, students need to:
- Multiplying decimals that go into the hundredths place.
- Use concrete models OR drawings.
- Use strategies based on either place value or the properties of operations.
- Relate the strategy to a written method.
- Explain their reasoning.
Woah!
Talk about needing to have a profound grasp of a concept.
This article will answer the following two questions. What does it mean to multiply decimals to the hundredths? How can I use concrete models or drawings with my students to help them understand this concept?
Decimals to the Hundredths Place
The hundredths place is the second digit to the right of the decimal point. We need to include multipliers and multiplicands that are whole numbers, in the tenths place and the hundredths place.
When we look at our other standards, we have only taught students to read and write decimals up to the thousandths place. As a result, here are the combinations of multipliers and multiplicands to use so that students can conceptually visualize the products.
- Whole numbers and tenths (ex: 5 x 0.4 or 0.4 x 5)
- Whole numbers and hundredths (ex: 5 x 0.23 or 0.23 x 5)
- Tenths and tenths (ex: 0.4 x 0.4)
- Tenths and hundredths (ex: 0.4 x 0.23 or 0.23 x 4)
If we set up problems that multiply hundredths and hundredths, the answer will be ten-thousandths, causing issues with modeling, reading, and writing the number.
Use Concrete Models or Drawings
Concrete models for decimals include place value blocks and decimal model multipliers. When drawing decimals, there are some ways to use student-created drawings, but printed decimal squares that we shade can be much more efficient.
Concrete Model: Place Value Blocks
When we are multiplying a decimal using models, we are finding a part of a part. I place a significant focus on the word “of” for these lessons. It can also help to relate this lesson to real-life items about which students are already familiar. For example, I love to make word problems about cake. Make sure that any example you use from real life can be cut evenly in multiple directions. (Think rectangles and squares instead of circles).
When modeling decimals multiplied by whole numbers, place value blocks come in handy. To keep your sanity and that of your students, I highly recommend keeping the whole number between 2-4. If you make the whole number large in these modeling examples, students will need many blocks, and the model will become unruly.
Concrete Model: Decimal Model Multipliers
The most accessible type of concrete model will be the decimal model multipliers. To use these, students find the solid, base decimal. Next, they overlay the transparent layer of the decimal they are multiplying by. The answer is the portion that is BOTH colors.
Drawings: Student Created Decimals
Students can create drawings of decimals. These drawings are the easiest to use when modeling the multiplication of a decimal by a whole number. For example, if I give the problem 0.42 x 5, students can draw five blobs, label each 0.42, and move on.
The difficulty with this strategy is that it does not lead the students towards the product for this problem. It does, however, demonstrate that they understand the meaning behind multiplying a decimal by a whole number.

I do NOT recommend encouraging or even allowing your students to draw their own decimal squares. It is simply not worth the time it takes. The squares will be inaccurate, students will be frustrated, and have difficulty interpreting their answers when using this method.
Drawings: Decimal Squares
Decimal squares are extremely helpful when teaching students to multiply decimals. They work great when multiplying any decimal by a whole number or multiplying tenths by tenths.
To use this strategy, students will need to have:
- A printout of decimal squares. (You can grab a free PDF of decimal squares here.)
- Colored pencils or highlighters
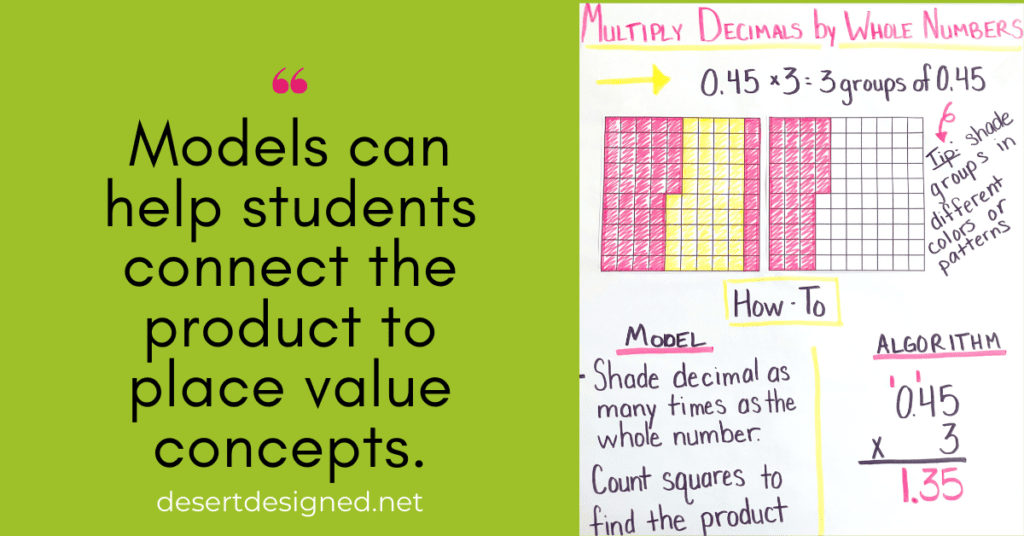
Multiply a Decimal by a Whole Number
For tenths by a whole number, begin with a tenths square. Shade the indicated number of tenths. Next, using different or alternating colors, continue shading the designated amount as many times as the whole number.
When multiplying hundredths by a whole number, the process is the same as above, but use a hundredths square rather than a tenths square.
Multiply a Decimal by a Decimal
When using models for multiplying decimals, I recommend sticking to tenths by tenths. Remember, the purpose of modeling isn’t just to get the answer. We are working with students to help them grasp the concept of what happens when we multiply decimals. If they explore enough with tenths, they should understand what is happening to the product and why it is smaller than the multiplier or multiplicand.
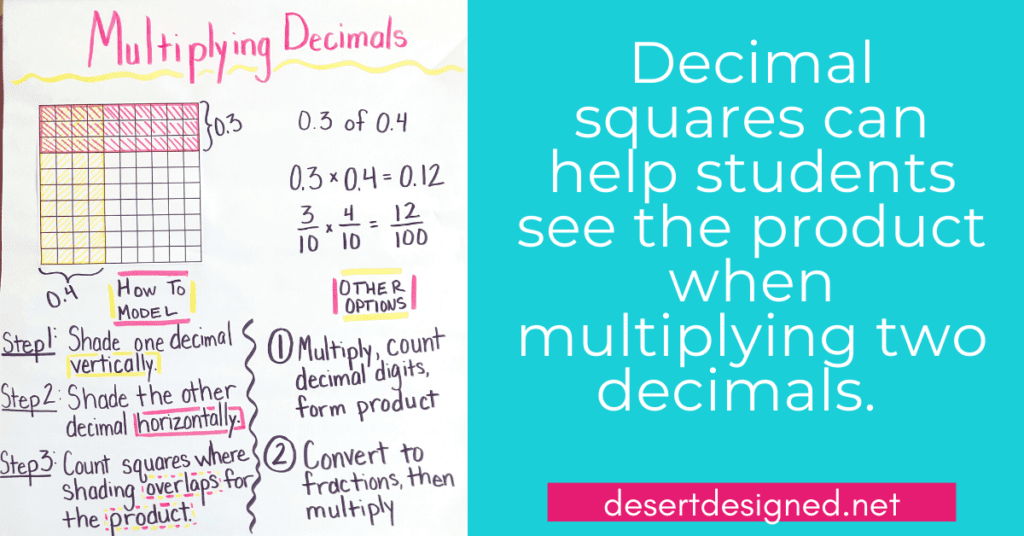
To model a decimal by a decimal, make sure you are using a hundredths square. First, shade in columns to show the first number of tenths. Next, in the opposite direction and a new color, shade rows to show the other number of tenths. The product will be the portion of the model that contains both colors.
Troubleshooting tip: Make sure students shade lightly, use highlighters, or use light-colored pencils for this activity.
The End Goal
Ultimately, we want to help our students have a firm grasp of understanding the decimal multiplication they are completing. Once they have a foundational concept of this multiplication, they can use strategies to complete these multiplication problems. Remember, this will take practice and patience.
Don’t forget to join my email list and download your free decimal model PDF resource!
I have many options in my Teachers Pay Teachers and Boom Learning Stores to help students practice decimal multiplication and lighten your load with problem and practice creation.